Growing Trays vs Other Plant Containers: Key Differences
2026-01-18 12:34:33
When it comes to plant propagation and nursery production, choosing the right container is crucial. Gardeners, horticulturists, and large-scale plant producers often face a choice between growing trays and other types of plant containers such as pots, tubs, and seedling trays. While both serve the purpose of housing plants, their design, functionality, and suitability for different growing conditions can vary significantly. Understanding these differences can help growers optimize plant health, improve production efficiency, and reduce costs.
What Are Growing Trays?
Growing trays, also known as seedling trays or propagation trays, are shallow, rectangular containers designed to hold multiple plants in individual cells. These trays are commonly made from plastic, though biodegradable options such as peat or coir are also available. The key features of growing trays include:
·Uniform cell size – ensures consistent growth for seedlings.
·Efficient drainage and aeration – prevents root rot and promotes healthy root development.
·Stackable design – ideal for nurseries and greenhouses to save space.
·Bulk production capability – manufacturers often produce these trays in large quantities to supply farms and garden centers.
Because of these characteristics, growing trays are particularly popular among commercial growers who require large-scale, uniform production of seedlings.


Comparison with Other Plant Containers
1. Pots and Tubs
Traditional pots and tubs are often deeper than growing trays and designed for individual plants. While they are versatile and suitable for mature plants, they have some limitations in large-scale seedling production:
·Less space-efficient – individual pots take up more room, making it harder to manage large quantities.
·Inconsistent growth – variations in soil volume can lead to uneven growth.
·Higher material cost – more plastic or clay is required per plant.
In contrast, growing trays allow growers to produce hundreds of seedlings in the same footprint as a few pots, reducing both space and material costs.
2. Seedling Trays vs Plug Trays
Seedling trays often refer to simple flat trays with multiple cells, while plug trays have slightly deeper cells designed for transplant-ready plants. The differences include:
·Cell depth – plug trays support stronger root development for transplanting, whereas shallow seedling trays are best for early germination.
·Transplanting efficiency – plug trays reduce transplant shock, improving survival rates.
Manufacturers offering bulk production of growing trays often include multiple cell sizes to cater to different plant species and growth stages.
3. Hydroponic Containers
Hydroponic systems use specialized containers for water-based growth. While efficient in nutrient delivery, they require precise monitoring of water quality, pH, and nutrient levels. Growing trays used in soil-based propagation are simpler to maintain and more flexible for traditional nursery setups.
Advantages of Growing Trays
1.Uniform Growth – Each plant develops in its own cell, preventing root entanglement and competition for nutrients.
2.Space Optimization – Stackable trays make it possible to maximize greenhouse or nursery space.
3.Production Efficiency – Ideal for manufacturers and factories needing bulk seedling production.
4.Cost Savings – Less material and soil per plant compared to individual pots.
5.Easy Handling and Transport – Lightweight trays allow for easier movement during the production process.
For companies involved in large-scale plant production, investing in growing trays directly from a factory or manufacturer ensures consistency in quality and supply, which is crucial for meeting production deadlines.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Container
While growing trays offer many advantages, it’s important to consider the following:
·Plant type – Some plants with deep root systems may require larger pots.
·Growth stage – Early-stage seedlings thrive in shallow trays, while mature plants need more soil volume.
·Production scale – Large-scale nurseries benefit most from stackable, modular trays.
·Material preferences – Plastic trays are durable and reusable, while biodegradable trays are more eco-friendly.
By carefully evaluating these factors, growers can select the most suitable container for their specific production needs.
Why Manufacturers Prefer Growing Trays
Growing trays are not just a convenience—they are a strategic choice for professional growers and manufacturers. Factories producing these trays emphasize:
·Bulk supply – Ensuring that nurseries can purchase large quantities without delays.
·Standardized quality – Uniform cell sizes and materials lead to predictable plant growth.
·Customizable options – Trays can be tailored for different plant species, cell counts, and dimensions.
Whether you are operating a commercial greenhouse or a small nursery, sourcing growing trays from a reliable manufacturer helps streamline production and improve overall efficiency.
Conclusion
When comparing growing trays with other plant containers like pots, tubs, and hydroponic setups, the advantages for large-scale seedling production are clear. They provide uniform growth, space efficiency, cost savings, and ease of handling. For manufacturers and nurseries seeking reliable bulk supply, growing trays are an essential investment that supports high-quality production.
Choosing the right container ultimately depends on your plant type, growth stage, and production scale. However, for those focused on efficient, uniform, and scalable propagation, growing trays remain unmatched in both design and functionality.
References
GB/T 7714:Gallegos J, Álvaro J E, Urrestarazu M. Container design affects shoot and root growth of vegetable plant[J]. HortScience, 2020, 55(6): 787-794.
MLA:Gallegos, Jesús, Juan E. Álvaro, and Miguel Urrestarazu. "Container design affects shoot and root growth of vegetable plant." HortScience 55.6 (2020): 787-794.
APA:Gallegos, J., Álvaro, J. E., & Urrestarazu, M. (2020). Container design affects shoot and root growth of vegetable plant. HortScience, 55(6), 787-794.

The CNC Seed Braiding Machine is a high-precision, fully automated agricultural equipment s...

It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...

The XP750 seeder has stable performance, excellent product quality, simple and convenient o...
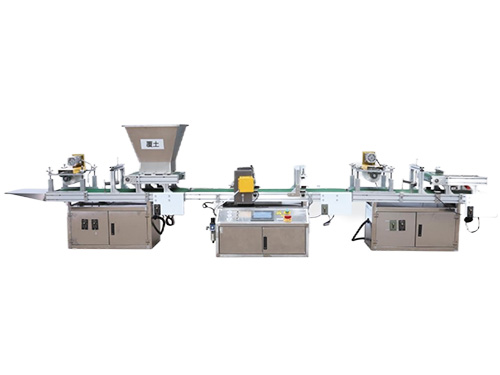
It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...