A Guide to Daily Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Seeders: Practical Tips for Extending Equipment Lifespan
2025-05-09 17:12:40
In agricultural production, seeders are crucial equipment for ensuring sowing efficiency and quality. However, prolonged use inevitably leads to various issues with the equipment, affecting its performance and service life. Proper daily maintenance of seeders and mastering troubleshooting skills not only guarantee the smooth progress of sowing operations but also effectively reduce usage costs.
I. Key Points for Daily Maintenance of Seeders
1.1 Post-operation Cleaning
Timely cleaning of the seeder after each sowing operation is an essential step. First, remove residual seeds, soil, fertilizer, and other debris from both the surface and interior of the equipment. If not cleaned promptly, this debris not only affects the equipment's appearance but may also corrode metal components, shortening the equipment's lifespan. Use tools such as brushes or high-pressure water guns to thoroughly clean key parts like the seed meter, furrow opener, and transmission components, ensuring no debris remains.
1.2 Component Lubrication and Maintenance
Regular lubrication and maintenance of the seeder's transmission components can effectively reduce friction between parts and lower wear. According to the equipment manual, apply appropriate lubricating oil or grease to parts such as chains, bearings, and gears. When adding lubricating oil, control the amount to avoid over- or under-lubrication. Additionally, check the quality of the lubricating oil. If it is found to be deteriorated or emulsified, replace it promptly.
1.3 Component Inspection and Tightening
Vibrations during operation may cause the connecting bolts of various seeder components to loosen, so it is necessary to regularly inspect the connections of all parts. Focus on checking bolts in areas such as the seed meter, furrow opener, and frame, tightening any that are loose. Also, check the tension of the drive belt. A belt that is too loose will reduce transmission efficiency, while one that is too tight will increase wear on the belt and transmission components. Adjust the tension to the appropriate level according to the equipment requirements.
1.4 Rust and Corrosion Prevention
When operating in the field, seeders are exposed to substances such as soil and moisture, making them prone to rusting. For parts prone to rust, such as the frame and furrow opener, apply anti-rust paint or oil after cleaning for protection. If slight rusting is found on the component surface, promptly sand it down and then apply anti-rust treatment to prevent further rust expansion.
II. Common Faults and Troubleshooting Methods for Seeders
2.1 Seed Meter Faults
2.1.1 Uneven Seed Dispensing
Uneven seed dispensing can lead to inconsistent crop emergence density, affecting later growth and yield. When this occurs, first check if there is debris blocking the seed meter and clear it if present. Next, verify if the adjusting components of the seed meter are functioning properly, such as whether the speed of the seed dispensing wheel and the size of the seed discharge opening meet the set requirements. Additionally, inconsistent seed shapes and sizes can also cause uneven dispensing, so ensure that seeds meeting the requirements are used.
2.1.2 No Seed Dispensing
When the seeder fails to dispense seeds, first check if the power transmission to the seed meter is normal. Inspect if the drive chain is broken or the belt is slipping. If the power transmission is normal, check if internal components of the seed meter are damaged, such as the seed dispensing wheel or seed scoop. Also, ensure that there is sufficient seed in the seed box and that the seeds are not bridging and blocking the seed discharge opening.
2.2 Furrow Opener Faults
2.2.1 Inconsistent Furrow Depth
Inconsistent furrow depth affects the sowing depth of seeds, thereby influencing germination rates and seedling growth. Check if the angle at which the furrow opener enters the soil is correct. An excessively large or small angle can result in unstable furrow depth. Additionally, the degree of wear on the furrow opener also affects furrow depth. Severely worn furrow openers should be replaced promptly. Moreover, uneven soil texture and uneven ground can also cause inconsistent furrow depth, which can be addressed by adjusting the seeder's suspension height or leveling the land.
2.2.2 Furrow Opener Blockage
During operation, the furrow opener may become blocked by weeds, soil, etc., affecting the furrowing effect. When blockage occurs, stop the operation and clear the debris from the furrow opener. Check if the structural design of the furrow opener is reasonable, such as whether there are parts prone to catching weeds, and make appropriate improvements if necessary. Also, cleaning the field before operation to reduce obstacles like weeds can effectively prevent furrow opener blockage.
2.3 Drive System Faults
Drive system faults can lead to poor power transmission in the seeder, affecting operational efficiency. Common drive system faults include chain breakage and belt slipping. Chain breakage is often due to long-term wear, excessive tension, or external force impacts. If a chain breaks, replace it with a new one promptly and adjust the tension appropriately. Belt slipping may be caused by belt wear, insufficient tension, or oil on the pulley surface. It can be resolved by replacing the belt, adjusting the tension, or cleaning the pulley surface.
III. Key Points for Long-term Storage Maintenance
When the seeder is not in use for an extended period, proper storage maintenance is crucial. First, conduct a comprehensive cleaning and maintenance of the equipment following the methods mentioned above for daily maintenance. Then, store the seeder in a dry, ventilated area, avoiding direct sunlight and rain. For some easily damaged components, such as the seed meter and furrow opener, they can be removed and stored separately to prevent deformation from being squeezed during storage. Additionally, start the seeder at regular intervals to run all components, preventing rusting and jamming due to prolonged inactivity.
IV. Conclusion
Proper daily maintenance and troubleshooting of seeders are key to ensuring their normal operation and extending their service life. By regularly cleaning, lubricating, inspecting, and tightening, and promptly identifying and resolving equipment issues, the probability of faults can be effectively reduced. Meanwhile, mastering the troubleshooting methods for common faults allows for quick and accurate identification and repair of issues when they arise, avoiding delays in the farming season. It is hoped that the practical tips introduced in this article can help you better maintain and use seeders, safeguarding agricultural production.

It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...

The XP750 seeder has stable performance, excellent product quality, simple and convenient o...
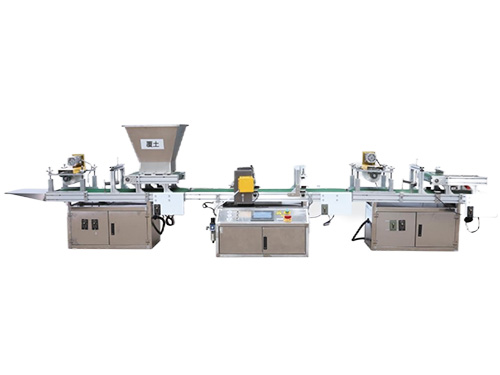
It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...

Needle list Seed nozzle model Different models Sowing types are different...