Secrets to Enhancing the Efficiency of Seed Drills: Operating Key Points and Field Management Strategies
2025-05-10 21:33:43
In the process of agricultural modernization, seed drills have become core equipment for improving sowing efficiency and ensuring timely farming operations. However, even when using the same type of seed drill, different operators can achieve significantly different levels of efficiency. Mastering scientific operating key points and field management strategies not only allows for the full utilization of a seed drill's performance but also reduces production costs, laying a solid foundation for a bountiful harvest.
I. Operating Key Points of Seed Drills
1.1 Precise Pre-operation Commissioning
Conducting a comprehensive and precise commissioning of the seed drill before starting work is a prerequisite for enhancing efficiency. First, adjust the sowing depth accurately according to the crop being planted and agronomic requirements. Both excessive and insufficient sowing depths can negatively impact seed germination and subsequent growth. The appropriate depth should be determined based on soil texture and seed characteristics. Second, set the sowing rate reasonably to ensure that the number of seeds per unit area meets the planting standards, avoiding seed waste or overly sparse sowing. Meanwhile, carefully inspect key components such as the seed metering device, furrow opener, and transmission system to ensure they operate smoothly and are securely connected, preventing malfunctions during operation.
1.2 Standardized Driving Operations
Standardized driving operations are crucial for improving sowing efficiency. While driving, maintain a constant and straight speed; it should not be too fast or fluctuate. A stable driving speed ensures uniform sowing, reducing issues like double sowing and missed sowing. Straight-line driving guarantees consistent row spacing, facilitating subsequent field management. Additionally, slow down in advance when making turns to prevent damage to the seed drill's components or a decline in sowing quality due to sharp turns.
1.3 Real-time Operation Monitoring
During the sowing operation, the operator should continuously monitor the working status of the seed drill. Pay attention to the seed discharge situation of the seed metering device. If problems such as uneven seed discharge or no seed discharge occur, stop the machine immediately to inspect and troubleshoot. At the same time, observe whether the depth and width of the furrow opened by the furrow opener meet the requirements, and make timely adjustments if abnormalities are found. Additionally, keep an eye on the operation of the transmission system, such as checking for loose chains or slipping belts, to ensure that all components of the seed drill work efficiently and in coordination.
II. Field Management Strategies
2.1 Optimization of Land Pre-treatment
Good land conditions are the foundation for the efficient operation of a seed drill. Before sowing, the land should be finely tilled to ensure that the soil is loose, flat, and free of large clods, weeds, and debris. Deep plowing can break the plow pan, increasing soil aeration and water retention. Harrowing can make the soil fine and crumbly, creating a suitable environment for seed germination. In addition, based on the soil fertility status, apply base fertilizers reasonably to improve soil fertility and provide sufficient nutrients for seedling growth.
2.2 Rational Planning of Operation Routes
Scientifically planning the operation routes of the seed drill can reduce empty travel distances and improve work efficiency. Before starting work, design reasonable driving routes based on the shape and size of the field. For regular-shaped fields, the shuttle sowing method can be adopted to reduce the number of turns at the field ends. This method involves the seed drill moving back and forth in straight lines across the field, similar to the motion of a shuttle in weaving, which helps to streamline the operation and minimize time wasted on turning.
For irregularly shaped fields, flexible planning is required to minimize repeated sowing or missed sowing as much as possible. A thorough analysis of the field's layout, including any obstacles, uneven terrain, or oddly shaped sections, should be conducted beforehand. You can break down the irregular field into smaller, more regular or semi-regular sub-sections and then plan individual routes for each. Start from a strategic point, such as a corner or an edge with easy access, and proceed through the sub-sections in a logical order, ensuring comprehensive coverage without unnecessary overlaps or gaps.
At the same time, arrange the operation sequence reasonably, giving priority to fields with better soil conditions or those that urgently need sowing. Fields with well-drained, fertile, and properly aerated soil can offer a more favorable environment for seed germination and early growth. By prioritizing these fields, you can take advantage of the optimal soil conditions to potentially achieve better crop establishment. Additionally, if there are fields facing time-sensitive factors, like approaching the optimal planting window or being at risk of adverse weather events, they should be sown first to ensure timely and successful crop cultivation.
2.3 Collaborative Operation with Supporting Facilities
Sowing operations often need to be carried out in conjunction with other supporting facilities, such as fertilizer application and film covering. Reasonably combining the seed drill with equipment such as fertilizer spreaders and film mulching machines to achieve integrated operations can significantly improve work efficiency. For example, side-deep fertilization during sowing can not only reduce the separate fertilization process but also increase fertilizer utilization. Prompt film covering after sowing can help retain soil moisture, increase soil temperature, and suppress weed growth.
III. Supporting Optimization for Efficiency Enhancement
3.1 Regular Equipment Maintenance and Care
Maintaining the seed drill in good technical condition is a guarantee for continuous and efficient operation. Regularly clean, lubricate, inspect, and tighten the seed drill, and promptly replace worn parts. Cleaning can prevent corrosion of the equipment caused by soil, seeds, and other debris. Lubrication reduces friction between components, lowering energy consumption. Inspection and tightening can avoid malfunctions caused by loose parts. Through regular maintenance and care, the service life of the seed drill can be extended, and its operational stability improved.
3.2 Skill Training for Operators
The professional skill level of operators directly affects the sowing efficiency of the seed drill. Regularly organize operators to participate in training to learn about the working principles, operating skills, and common troubleshooting methods of the seed drill. Operators with proficient skills can more accurately adjust the equipment, operate it in a standardized manner, and promptly identify and solve problems that arise during operation, thereby improving overall work efficiency.
IV. Conclusion
Improving the sowing efficiency of a seed drill is a systematic project that encompasses scientific operating key points, reasonable field management strategies, and comprehensive supporting optimization measures. By precisely commissioning the equipment, standardizing driving operations, optimizing land conditions, rationally planning operation routes, and combining these with regular maintenance and operator skill training, the performance advantages of the seed drill can be fully utilized, achieving efficient sowing.

The CNC Seed Braiding Machine is a high-precision, fully automated agricultural equipment s...

It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...

The XP750 seeder has stable performance, excellent product quality, simple and convenient o...
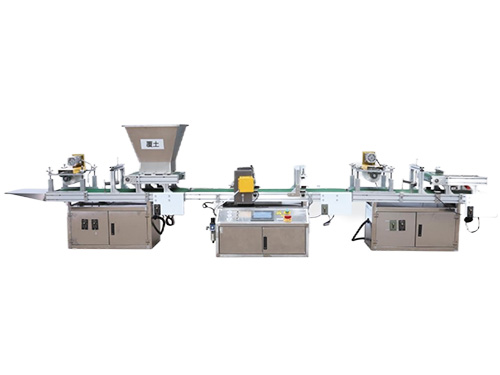
It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...