Key Factors for Choosing Seedling Trays: Essential Knowledge for Beginners
2025-04-20 12:33:57
I. Introduction
Seedling trays are the first step towards efficient seedling cultivation, but with a wide array of options on the market, beginners often find themselves overwhelmed by the choices. This article breaks down the core elements of selection to help you accurately match your needs and avoid common pitfalls.
II. Basic Understanding of Seedling Trays
2.1 Definition and Function
Seedling trays are standardized, partitioned containers used for centralized cultivation of young plants. They enable categorized sowing of seeds and isolated root growth through individual cells.
2.2 Development Trends
From traditional wooden shallow trays to modern plastic plug trays, materials have evolved towards lightweight and durability. Structures now incorporate functional designs such as self-watering features and accommodation for deep root systems.
III. Three Core Dimensions for Selection
3.1 Matching Planting Needs
Selection for Vegetable Cultivation
Deep-rooted crops (e.g., tomatoes, okra): Opt for deep-celled trays with a depth of ≥8 cm.
Shallow-rooted leafy greens (e.g., lettuce, spinach): Suitable for shallow, wide general-purpose trays.
Key Points for Flower Cultivation
Small annual flowers (e.g., petunias, lobelia): Prioritize 72-128-cell small-hole trays.
Large perennial flowers (e.g., hydrangeas, peonies): Require large-diameter deep trays to support root expansion.
3.2 Balancing Budget and Cost-Effectiveness
Material Priority: PP plastic offers resistance to aging and wear; PS foam is lightweight but prone to breakage, making it suitable for short-term use.
Avoid Overconsumption: General-purpose shallow trays are versatile for most scenarios; upgrade to specialized trays as needed.
3.3 Quality Detail Checks
Substrate Thickness: Ensure no significant indentation when pressing the edges, confirming load-bearing capacity.
Drainage Design: Uniform bottom hole placement with appropriate hole diameter to prevent waterlogging and root rot.
IV. Pitfalls to Avoid for Beginners
4.1 Specification Misconceptions
Avoid "One Tray Fits All": Small seeds require small-hole trays, while large seeds need larger cells.
Allow for Growth Space: Prevent overcrowding and leggy growth by selecting trays based on the mature plant size.
4.2 Material Traps
Reject Recycled Materials: Low-quality plastics are prone to brittleness and may release harmful substances.
Low-Temperature Suitability: Northern users should confirm material resistance to freezing.
V. Conclusion: Choosing the Right Tray = Winning at the Starting Line
Selecting seedling trays requires consideration of plant characteristics, budget, and quality. Remember the three principles of "matching root systems, ensuring proper drainage, and selecting high-quality materials," and even beginners can easily take the first step towards scientific seedling cultivation. Start by assessing your needs and choosing your dedicated seedling tray today!

The CNC Seed Braiding Machine is a high-precision, fully automated agricultural equipment s...

It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...

The XP750 seeder has stable performance, excellent product quality, simple and convenient o...
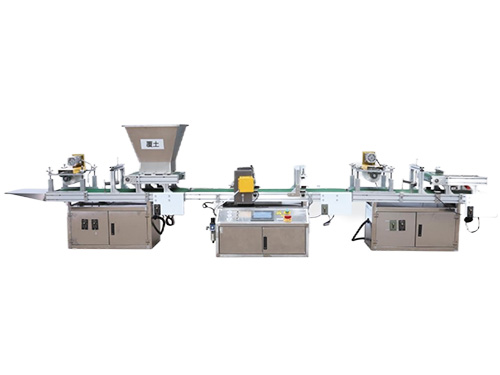
It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...