Proper Usage of Seedling Trays: Boosting Seedling Efficiency Significantly
2025-04-19 10:46:37
I. Introduction
In modern horticultural and agricultural seedling cultivation systems, seedling trays are pivotal tools determining seedling survival rates and growth quality. From selecting suitable options to daily maintenance, precise operations in every step directly impact seedling efficiency. This article systematically dissects the entire process of using seedling trays, providing scientific and practical guidance for growers.
II. Basic Understanding of Seedling Trays: Definition and Evolution
2.1 Definition
A seedling tray is a standardized container used for centralized cultivation of plant seedlings. Through compartmentalized designs, it enables categorized seed sowing and individual seedling management, widely applied in large-scale seedling cultivation of vegetables, flowers, and cash crops.
2.2 Evolution
From early wooden or terracotta shallow trays to modern PP plastic plug trays and PS foam seedling trays, material iterations balance durability and cost control. Structures have evolved from simple shallow trays to deep-compartment, self-watering, and other functional designs to meet different plant root growth needs.
III. Core Values of Seedling Trays
3.1 Efficiency Enhancement
Standardized sizes fit sowing machines and transplanting equipment, saving labor through batch operations. Compartmentalized structures simplify sorting processes.
3.2 Optimized Growth Environment
Independent compartments isolate disease transmission, precisely control substrate moisture and root space, reducing disease risks.
3.3 Flexible Management
Stackable and movable features facilitate environmental control in greenhouses and sheds, making categorized seedling cultivation more efficient.
IV. Key Considerations for Purchase: Matching Plants and Budget
4.1 Selection Based on Cultivation Needs
Vegetable Seedlings: Deep-rooted crops require deep-compartment trays (depth ≥8cm), while leafy vegetables suit shallow trays.
Flower Seedlings: Small-flower bedding plants use small-hole trays, while large flowers need large-diameter deep trays.
4.2 Budget and Quality Balance
Material Preferences: PP plastic is durable and aging-resistant, while PS foam is lightweight but prone to breakage.
Detail Checks: Pay attention to substrate thickness and drainage hole density to avoid waterlogging and root rot.
V. Comprehensive Operation Guide for Usage
5.1 Preparation Phase
Cleaning and Disinfection: Remove residual substrate with a soft brush, soak in diluted bleach for 30 minutes, and air-dry to prevent mold.
Substrate Preparation: Adjust universal formulas (peat moss + vermiculite + perlite) as needed, adding leaf mold for acid-loving plants.
5.2 Sowing Practices
Depth Control: Cover large seeds with soil twice their diameter; gently press small seeds into the substrate.
Density Planning: 1-2 seeds per compartment, following the principle of "sparser is better."
Moisture Retention Tips: Cover lightly with 0.5-1cm of substrate; use fine mist spraying or bottom watering.
5.3 Seedling Management
Light Adjustment: Weak light during germination, 6-8 hours of direct sunlight during growth.
Temperature Control: 20-25°C for heat-loving plants, 15-20°C for cold-tolerant ones.
Fertilization Strategy: Balanced fertilizer initially, increased nitrogen during growth, and emphasis on phosphorus and potassium during hardening.
VI. Maintenance and Care: Prolonging Lifespan
6.1 Cleaning and Disinfection Cycle
Remove residual substrate after use, thoroughly disinfect after each batch to block disease transmission.
6.2 Scientific Storage Methods
Stack with soft paper padding to prevent compression; store deep trays vertically.
Keep dry and away from light; avoid proximity to fertilizers and pesticides.
VII. Common Problem Solutions
7.1 Seedling Legginess
Increase light duration, lower nighttime temperatures, and control watering.
7.2 Disease Prevention
Strictly follow disinfection procedures, isolate diseased plants, and apply targeted fungicides.
7.3 Poor Root Development
Check substrate permeability, ensure drainage holes are unobstructed, and avoid waterlogging.
VIII. Conclusion
From understanding principles to practical details, proper use of seedling trays is the cornerstone of efficient seedling cultivation. Mastering the methods outlined here not only enhances seedling robustness but also significantly shortens cultivation cycles. Take immediate action to embark on a productive seedling cultivation journey with scientific practices!

The CNC Seed Braiding Machine is a high-precision, fully automated agricultural equipment s...

It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...

The XP750 seeder has stable performance, excellent product quality, simple and convenient o...
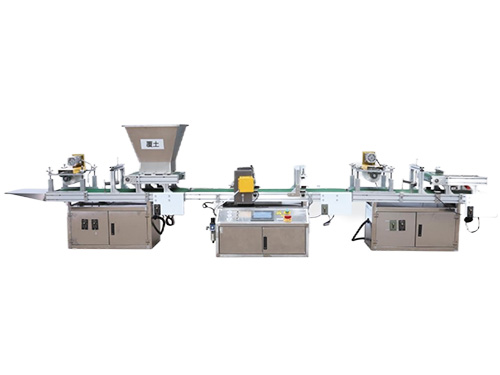
It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...