Unveiling the Secrets of Seed Trays vs. Seedling Trays: Choose Right, Grow Efficiently
2025-03-27 17:06:27
In the realm of cultivation, whether it's large-scale agricultural production or enjoyable home gardening, sowing and seedling cultivation are foundational yet critical steps. Seed trays and seedling trays, as essential tools in these processes, directly impact the success of seedling work. Selecting the appropriate trays can streamline the seedling process, significantly boost efficiency, and lay a solid foundation for robust plant growth.
I. Basic Understanding of Seed Trays and Seedling Trays
1.Definitions and Appearance
Seed trays are specialized containers designed to provide an initial sowing environment for seeds. Commonly shaped as regular rectangles or squares, they facilitate neat arrangement in limited spaces and maximize space utilization. Sizes range from compact trays suitable for windowsill gardening to large trays meeting mass cultivation needs. Colors include black, white, and transparent. Black trays absorb heat well, aiding seed germination in cooler environments; white trays reflect light to prevent overheating; transparent trays allow easy monitoring of seed germination and growth.
Seedling trays are used for nurturing seedlings after germination. Deeper than seed trays, they accommodate root growth during the seedling stage. Shapes and sizes vary to suit different plant seedlings. Color functions are similar to seed trays, allowing growers to choose based on their environment and needs.
2.Material Types
Plastic: Plastic trays dominate the market due to their lightweight nature, reducing labor intensity during handling. They are durable, withstand multiple uses and harsh conditions, and are cost-effective for large-scale users.
Wood: Wooden trays offer natural breathability, promoting soil aeration for seeds and seedlings. Ideal for plants requiring high air circulation, they also add an eco-friendly aesthetic to gardens.
Biodegradable Materials: Aligning with eco-conscious trends, biodegradable trays made from plant fibers or starch decompose naturally after use, reducing soil and water pollution. They meet planting needs while supporting sustainability.
II. Detailed Types of Seed Trays and Seedling Trays
1.Standard Single-Cell Trays
Seed Trays: Simple, undivided structure suits large seeds or those needing ample space. Suitable for large flower seeds like sunflowers, offering easy sowing.
Seedling Trays: Deeper single-cell trays provide sufficient root space for seedlings that grow quickly without frequent transplanting, such as cabbage seedlings.
2.Divided Trays
Seed Trays: Divided into small cells for sowing different seed varieties or batches. Prevents seed mixing and ensures proper spacing for nutrient, water, and light access. Ideal for vegetable seeds like tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers.
Seedling Trays: Isolated cells prevent disease spread and facilitate targeted care. Enhances efficiency in large-scale operations by enabling precise management.
3.Covered Trays
Seed Trays: Lids retain humidity, regulate temperature, and block pests, creating a stable microenvironment for sensitive seeds like orchids.
Seedling Trays: Lids maintain soil moisture, protect seedlings from cold, dust, and pests, improving survival rates.
III. Applications in Different Scenarios
1.Home Gardening
Seed Trays: Compact trays fit balconies or windowsills, simplifying sowing for novices. Ideal for flower variety trials.
Seedling Trays: Divided designs manage seedlings efficiently, preparing them for transplanting. Suitable for vegetables like cilantro and scallions.
2.Professional Agriculture
Seed Trays: Standardized for bulk operations, enabling efficient large-area sowing of crops like wheat and corn.
Seedling Trays: Facilitate mechanized operations and record-keeping, supporting high-efficiency seedling production.
3.Nursery Operations
Seed Trays: Divided designs meet diverse seed sowing needs, preventing mix-ups for rare flowers.
Seedling Trays: Integrated with irrigation systems, they provide optimal growth conditions for large-scale seedling production.
IV. Advantages of Seed Trays and Seedling Trays
1.Enhanced Efficiency
Seed Trays: Save time with standardized layouts, enabling batch operations.
Seedling Trays: Streamline management through divided cells, improving space utilization and operational efficiency.
2.Improved Germination and Seedling Quality
Seed Trays: Optimal spacing ensures resource access, with material choices optimizing moisture and air circulation.
Seedling Trays: Adequate root space and stable environments boost seedling health and survival.
3.Ease of Management and Transplanting
Seed Trays: Neat arrangements simplify monitoring and transfer to seedling trays.
Seedling Trays: Clear cell divisions reduce root damage during transplanting, aiding survival.
V. Purchasing Considerations
1.Size and Type Based on Needs
Seed Trays: Choose compact for home use, large for agriculture. Select divided or covered trays based on seed variety and environmental needs.
Seedling Trays: Match size to seedling growth requirements. Use divided trays for large-scale operations.
2.Material Quality Assessment
Seed Trays: Check plastic thickness, wood durability, and biodegradable material standards.
Seedling Trays: Prioritize non-toxic, sturdy plastics or well-treated wood. Ensure biodegradable trays meet durability needs.
3.Brand and Price Factors
Seed Trays: Opt for reputable brands with quality assurance. Balance budget and performance.
Seedling Trays: Choose brands with design and manufacturing expertise. Negotiate prices for bulk purchases while ensuring quality and service.
VI. Market Trends and Outlook
1.Industry Development Overview
The seed tray and seedling tray market is expanding, driven by agriculture, nurseries, and home gardening. Diverse products meet various needs, with manufacturing hubs and e-commerce channels rising.
2.Technological Innovation Directions
New Materials: Develop breathable, moisture-retentive, and durable eco-materials with antimicrobial properties.
Smart Designs: Integrate auto-watering, fertilization, and environmental control systems for precision cultivation.
3.Impact on Future Cultivation
Efficiency and Quality: Innovative trays will enhance productivity, reduce pests, and improve plant health.
Sustainability: Biodegradable trays will reduce environmental impact, aligning with green trends.
Diverse Needs: Technological advancements will cater to both large-scale efficiency and home gardening aesthetics, driving industry diversification.
VII. Conclusion
Seed trays and seedling trays play pivotal roles in cultivation. By understanding their types, advantages, purchasing tips, and market trends, growers can make informed choices, achieving efficient seedling cultivation. As technology advances, these trays will bring more convenience to the planting industry, fostering sustainable and intelligent agricultural development.

It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...

The XP750 seeder has stable performance, excellent product quality, simple and convenient o...
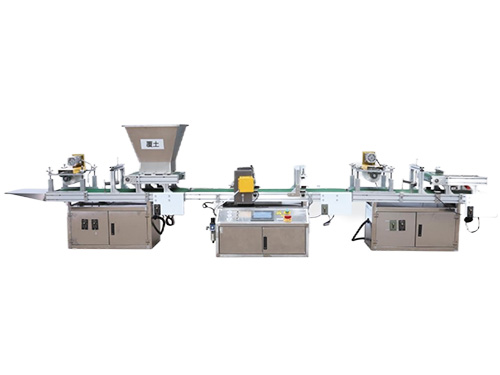
It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...

Needle list Seed nozzle model Different models Sowing types are different...