How Many Seeds Should You Plant Per Seedling Tray for Maximum Growth and Health?
2025-02-11 02:36:44
Introduction: The Importance of Proper Seedling Tray Planting
When starting a garden or greenhouse, one of the most common questions is how many seeds should be planted per seedling tray to ensure maximum growth and plant health. Overcrowding can stunt the growth of seedlings, while too few seeds might lead to wasted space. The key to achieving healthy, thriving plants lies in understanding the right seed-to-tray ratio, the specific needs of the plants being grown, and how to maintain optimal growing conditions. This guide will help you determine the ideal number of seeds to plant per seedling tray based on plant types, growth habits, and tray sizes.
Understanding Seedling Tray Size and Cell Configuration
1. Standard Seedling Tray Sizes
Seedling trays are available in various sizes and configurations, with the most common being the 72-cell, 128-cell, or 200-cell trays. These trays are designed to hold individual seedlings, each occupying its own cell. The size of the cell determines how much space is available for each plant's roots to grow. For larger plants like tomatoes or peppers, fewer seeds per cell are needed, whereas smaller plants such as herbs or lettuce can be grown in more densely packed trays.
2. Cell Size and Plant Type
The size of each individual cell within the tray plays a significant role in determining how many seeds to plant. Larger seeds such as cucumbers, squash, and melons require more space for root growth and should be planted in trays with larger cells or fewer seeds per cell. Smaller seeds, such as those for herbs and leafy greens, can be planted more densely in smaller cells. Generally, plants with shallow root systems like lettuce, basil, and spinach can tolerate being closer together than plants with deep or large root systems.
Determining the Right Number of Seeds per Cell
1. Small Seeds and Dense Planting
For small seeds, like those of herbs, leafy greens, or flowers, it is often recommended to plant 2–3 seeds per cell, especially if you're aiming for a higher germination rate. This gives the seeds a better chance to sprout. After germination, the weaker or excess seedlings can be thinned out to allow the strongest plant to continue growing. This approach ensures that you don't end up with empty cells in case some seeds fail to germinate.
2. Larger Seeds and Spacing Needs
Larger seeds, such as tomatoes, peppers, and squash, should generally be planted one seed per cell. These seeds require more space for their roots to spread out, and overcrowding can lead to competition for nutrients, water, and sunlight, ultimately resulting in weak seedlings. Giving them more room ensures that they receive all the resources they need for strong and healthy growth.
3. Consider Growth Rates and Planting Depth
Another factor to consider is the growth rate and planting depth of the seeds. Faster-growing plants, such as radishes and lettuce, can be planted more densely, as they require less space to establish strong root systems. On the other hand, slower-growing plants like tomatoes and peppers need ample space to grow and develop properly. If seeds are planted too deep or too close together, they may not receive enough light or oxygen, which can inhibit healthy root and stem development.
Factors That Affect Seedling Tray Planting Density
1. Plant Growth Habit
Different plants have different growth habits, which affect how many seeds can be planted per cell. For instance, plants with sprawling or vining growth habits, such as cucumbers and pumpkins, require more space and should only have one seed planted per cell. Compact plants with an upright growth habit, like herbs or leafy greens, can tolerate closer spacing. Understanding your plant’s growth habit will help you determine the best spacing for each variety.
2. Climate and Environmental Conditions
The environment in which seedlings are grown also affects planting density. If you're growing seeds in a greenhouse, where environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light are controlled, you may be able to plant seeds more densely. However, if you are growing seedlings outdoors or in less controlled conditions, you may need to give your plants more space to avoid competition for resources, especially when dealing with fluctuating environmental factors.
3. Germination Rate and Seed Quality
The germination rate of your seeds is also an important factor in deciding how many seeds to plant. Seeds with a lower germination rate may require you to plant a few extra per cell to ensure successful sprouting. On the other hand, high-quality seeds with a high germination rate might only require one or two per cell. Checking the seed packet for information on the expected germination rate can help you decide how many seeds to plant.
Thinning and Transplanting for Maximum Growth
1. Thinning Seedlings for Optimal Growth
Once the seedlings begin to grow and develop their first true leaves, thinning is necessary. This process involves removing the weaker or overcrowded plants to allow the remaining seedlings to receive adequate space, light, and nutrients. If you’ve planted too many seeds per cell, thinning ensures that the remaining plants can thrive without competition.
2. Transplanting Seedlings into Larger Spaces
As the seedlings grow and their roots begin to outgrow the cell, they should be transplanted into larger pots or garden beds. Overcrowded seedlings may struggle to establish themselves and could suffer from stunted growth. Transplanting at the right time ensures that the seedlings have enough space to grow into mature plants, allowing for maximum growth potential and overall plant health.
Tips for Successful Seedling Tray Planting
1. Use High-Quality Seed Starting Mix
A good quality seed-starting mix is essential for successful germination and healthy seedling development. Choose a mix that is well-draining, lightweight, and free of contaminants. Avoid using regular garden soil, as it can be too dense and may harbor pests or diseases.
2. Maintain Consistent Watering
Proper watering is essential during the seedling stage. Keep the soil moist but not waterlogged, and avoid letting the seedlings dry out. Watering from the bottom of the tray using a shallow tray can prevent the seeds from becoming dislodged. Using a spray bottle to mist the soil can also help maintain the right moisture level without disturbing the seeds.
3. Provide Adequate Lighting
Seedlings require adequate light to grow strong and healthy. If you’re growing your seedlings indoors, consider using grow lights to ensure they receive the necessary light for photosynthesis. Make sure the trays are positioned in an area where they can receive sufficient natural light, or supplement with artificial lighting if needed.
Conclusion: Finding the Right Seed-to-Tray Ratio for Healthy Growth
The number of seeds you should plant per seedling tray depends on a variety of factors, including the size of the seed, plant growth habits, and the specific needs of the plants you are growing. Small seeds can generally be planted more densely, while larger seeds need more space to grow. By understanding your plants’ needs, thinning out excess seedlings, and transplanting at the right time, you can maximize the growth and health of your seedlings. Following these guidelines will help you create a thriving garden, whether you're growing vegetables, herbs, or flowers.

It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...

The XP750 seeder has stable performance, excellent product quality, simple and convenient o...
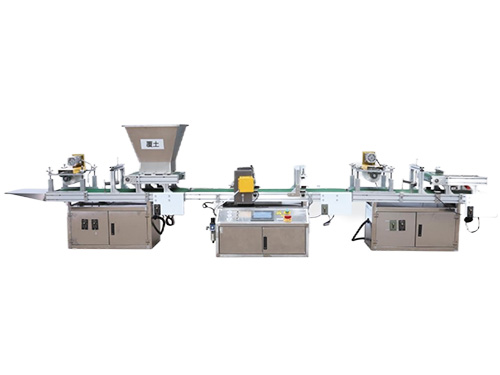
It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...

Needle list Seed nozzle model Different models Sowing types are different...