When to Transplant Seedlings from a Seed Tray: A Comprehensive Guide for Optimal Growth
2025-01-08 02:40:29
Transplanting seedlings from a seed tray is a crucial step in the gardening process. Knowing the right time to transplant your seedlings can determine their overall health, growth success, and yield. Transplanting too early or too late can result in weak plants, stunted growth, and even plant loss. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore when to transplant seedlings from a seed tray, key indicators to watch for, and best practices to ensure optimal growth and success.
Why Timing Matters When Transplanting Seedlings
Transplanting seedlings at the right time is essential for several reasons:
Promotes Strong Root Development
Roots are the foundation of healthy plants. Transplanting at the appropriate time encourages robust root growth, which helps plants absorb nutrients and water more effectively.
Reduces Transplant Shock
Transplant shock occurs when plants experience stress from being moved to a new environment. Proper timing minimizes shock, ensuring that plants adapt quickly and continue growing.
Improves Plant Health and Productivity
Healthy seedlings that are transplanted at the right time grow stronger and more vigorously. This leads to better plant health, increased yield, and higher productivity.
Key Factors to Determine When to Transplant Seedlings from a Seed Tray
Several indicators and factors will help you determine when it's time to transplant your seedlings from a seed tray into larger containers or garden beds.
1. Size of Seedlings
One of the most critical indicators is the size of your seedlings.
· True Leaves Development:
After your seeds have germinated, seedlings will initially grow cotyledons (the first set of leaves). Once your seedlings develop their first set of true leaves, it's a good sign that they are ready to be transplanted. True leaves are a clear indicator that your plants have established some roots and can support their growth beyond the seed tray.
· Height and Density:
When seedlings become tall and start to overcrowd the seed tray compartments, it's a sign that they need more space to grow. Transplanting them at this point allows each plant to have adequate room for root expansion and access to nutrients.
2. Root Growth and Health
Healthy roots are essential for successful transplanting.
· Root Bound Seedlings:
If you notice roots growing out of the drainage holes at the bottom of the seed tray, it means your seedlings are root-bound. Root-bound plants can become stressed, as their roots are overcrowded and competing for nutrients. This is a strong sign that it's time to transplant them.
· Root Visibility:
Roots that look dense and healthy inside the seed tray compartments also indicate that the seedlings need more space to expand and absorb nutrients from the soil.
3. Temperature and Weather Conditions
Temperature and environmental conditions play a crucial role in determining when to transplant seedlings.
· Optimal Outdoor Temperatures:
Most seedlings can be transplanted outdoors when the risk of frost has passed, and soil temperatures are consistently warm. For most vegetables, this usually occurs in late spring or early summer.
· Indoor to Outdoor Transition:
If you start your seedlings indoors, it's best to gradually harden them off before transplanting. Expose seedlings to outdoor conditions gradually over 7-10 days, ensuring they acclimate to temperature fluctuations, wind, and sunlight.
4. Plant Type and Growth Stage
Different plant species have different transplanting requirements and ideal timelines.
· Vegetables:
For popular vegetables like tomatoes, peppers, and broccoli, transplant them once they have at least two to three sets of true leaves. This ensures that they have a well-established root system and are ready to handle outdoor growth conditions.
· Flowers and Herbs:
Many flowers and herbs can be transplanted once they have strong roots and healthy growth. For most annual flowers and herbs, transplanting once they develop their first true leaves and grow a few inches tall is typically ideal.
Step-by-Step Guide to Transplanting Seedlings from a Seed Tray
Step 1: Prepare the New Growing Space
Choose an appropriate growing space, whether it’s larger pots, garden beds, or raised containers. Ensure that the soil or growing medium is rich in nutrients, well-draining, and contains organic matter.
Step 2: Water the Seedlings
Water your seedlings about an hour before transplanting. Moist soil helps reduce transplant shock and supports the roots during the transition.
Step 3: Gently Remove Seedlings from the Tray
Carefully remove seedlings from the seed tray compartments, ensuring minimal disturbance to their roots. Use your fingers or a small tool to gently loosen the roots and lift each plant.
Step 4: Plant the Seedlings in the New Space
Plant each seedling at the same depth it was growing in the seed tray. Firm the soil around the roots gently but not too tightly, as compact soil can damage the roots.
Step 5: Water Thoroughly
After planting the seedlings in their new space, water them thoroughly. This helps settle the soil around the roots and provides an initial boost of hydration.
Step 6: Provide Shade if Necessary
If transplanting seedlings during hot or sunny conditions, consider providing temporary shade for a few days. Use shade cloth or place seedlings in a slightly shaded area to protect them from excessive heat and sun exposure.
Tips for a Successful Transplanting Process
Gradually Hardening Off Seedlings
If your seedlings were started indoors, spend 7-10 days hardening them off by placing them outside for a few hours each day. Gradually increase their exposure to sunlight, wind, and varying temperatures.
Monitor Transplant Shock Symptoms
Look out for signs of transplant shock, such as wilting leaves, yellowing stems, or stunted growth. Providing consistent water, avoiding extreme temperatures, and offering light shading can help seedlings recover quickly.
Choose the Right Tools
Use garden tools like tweezers, a transplanting fork, or small hand trowels to minimize root disturbance and improve the efficiency of your transplanting process.
Conclusion
Knowing when to transplant seedlings from a seed tray is a critical aspect of gardening success. By observing your seedlings’ growth stages, size, root health, and environmental conditions, you can make informed decisions about when to move your plants to larger containers or garden beds. Transplanting at the right time promotes healthy root growth, reduces transplant shock, and ultimately boosts plant productivity and health.
Follow these guidelines, observe your plants carefully, and adjust your transplanting techniques as needed. With proper timing and care, your seedlings will thrive, grow vigorously, and contribute to a productive and successful gardening season.

It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...

The XP750 seeder has stable performance, excellent product quality, simple and convenient o...
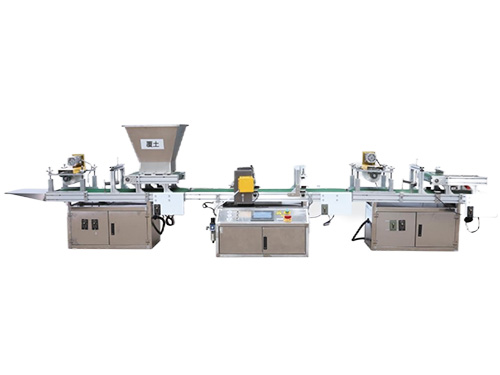
It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...

Needle list Seed nozzle model Different models Sowing types are different...