Unveiling the Seedling Seeder : A Comprehensive Overview of Its Working Principle, Usage Advantages, and Key Points for Purchase Avoidance
2025-06-10 01:08:39
I. Introduction
Against the backdrop of the rapid development of the modern planting industry, Seedling Seeders have gradually become an indispensable and crucial piece of equipment in the fields of agriculture and horticulture. Whether it's for the meticulous planting in a small home vegetable garden or the large-scale production on a major farm, they play a vital role. This article will delve deeply into the working principle and notable advantages of Seedling Seeders, and provide users with practical guidance on how to avoid pitfalls when purchasing, helping everyone to better select and utilize this efficient tool.
II. What is a Seedling Seeder : Definition and Evolution
(A) Clear Definition
A Seedling Seeder is a device specifically designed for sowing seeds during the seedling stage. Through specific mechanical structures or technologies, it precisely scatters seeds into seedling substrates or soil, effectively controlling the sowing quantity, depth, and spacing of the seeds, thereby creating favorable conditions for seed germination and seedling growth.
(B) Development History
Early Seedling Seeders had simple structures and were mostly manually operated, relying on human labor to complete the sowing process, which was inefficient and had limited precision. With technological advancements, modern Seedling Seeders now utilize more durable materials such as metals or engineering plastics, and their structural designs have been continuously optimized. They have evolved from manual models to semi-automatic and fully automatic ones. Additionally, the integration of intelligent technologies has equipped sowers with functions like automatic monitoring and precise adjustment, greatly enhancing sowing efficiency and quality.
III. Detailed Explanation of the Working Principle of Seedling Seeders
(A) Manual Sower Principle
Manual sowers mainly consist of components such as a seed box, a seed dispensing mechanism, and a handle. During operation, by manually pressing, rotating, or pushing the handle, the seed dispensing mechanism is driven to move, causing the seeds to fall from the seed box into the sowing holes in a certain pattern. For example, in a common drum-type manual sower, the drum is equipped with dimples of different sizes. As the drum rotates, the dimples carry the seeds, and when they reach a specific position, the seeds fall into the sowing holes under gravity, achieving single or multiple seed sowing.
(B) Semi-Automatic and Fully Automatic Sower Principles
Semi-automatic sowers usually employ small power devices (such as motors) to assist in seed dispensing, reducing the intensity of manual labor. Fully automatic sowers integrate multiple functional modules such as trenching, sowing, covering soil, and pressing. Taking a pneumatic fully automatic sower as an example, it uses vacuum suction to adhere seeds to the suction holes on a seed dispensing plate. When the plate rotates to the sowing position, the vacuum is cut off or air is blown to make the seeds fall into the sowing trench. Subsequent components then complete tasks like covering soil and pressing, with a high degree of automation throughout the process, significantly improving sowing efficiency and precision.
IV. Notable Advantages of Using Seedling Seeders
(A) Significantly Improved Sowing Efficiency
Traditional manual sowing is slow and inefficient. In contrast, Seedling Seeders, with their standardized and mechanized operations, can quickly complete a large number of sowing tasks. Whether it's on a vast farmland or in a small seedling greenhouse, they can achieve efficient sowing in a short time, saving a substantial amount of labor and time costs.
(B) Guaranteed Sowing Precision
Sowers can precisely control the number of seeds per hole, sowing depth, and row spacing. An appropriate sowing depth helps seeds absorb water and nutrients, ensuring germination rates. Uniform row spacing provides sufficient space for seedling growth, avoiding poor growth due to overcrowded planting, thereby improving the overall quality of the seedlings.
(C) Reduced Labor Intensity
Semi-automatic and fully automatic sowers reduce manual labor. Operators no longer need to bend over for long periods or perform repetitive mechanical motions, decreasing physical exertion. Even manual sowers are designed with ergonomics in mind, making operation easier and more convenient, suitable for users of different ages and physical conditions.
(D) Suitable for Various Planting Scenarios
From home gardening and small nurseries to large commercial farms, and from vegetable and flower planting to grain crop sowing, there are corresponding models and types of Seedling Seeders available. Additionally, some sowers can adapt to different terrains and soil conditions, such as slopes and sandy soils, expanding the scope and flexibility of planting.
V. Key Points for Avoiding Pitfalls When Purchasing Seedling Seeders
(A) Selecting the Type Based on Planting Needs
Planting Scale: For home planting or small-scale seedling raising, manual or small semi-automatic sowers can be chosen for their simple operation and low cost. Large farms or professional seedling bases, on the other hand, require fully automatic and high-efficiency sowers to meet the demands of large-scale production.
Crop Type: Different crops have seeds of varying sizes, shapes, and sowing requirements. For example, vegetable seeds are relatively small and suitable for precision sowers, while larger seeds like corn and soybeans can choose sowers with a larger seed dispensing capacity.
(B) Paying Attention to Product Quality and Performance
Material and Craftsmanship: High-quality sowers should be made of sturdy and durable materials, such as thickened metal frames and wear-resistant engineering plastic components. The welding should be firm, with no obvious flaws. Check the processing precision of key parts like the seed dispensing mechanism and transmission components to ensure smooth operation.
Functions and Adjustability: The sower should have functions like seed dispensing quantity adjustment, sowing depth adjustment, and row spacing adjustment, with convenient and precise adjustment operations. Some high-end models may also have additional functions like seed screening and automatic alarms, which can be selected according to actual needs.
(C) Considering Budget and After-Sales Service
Price Range: There are significant price differences among Seedling Seeders of different brands, types, and functions. Within the budget, prioritize products with high cost-effectiveness, avoiding the pursuit of low prices at the expense of quality, and there is no need to blindly buy high-priced products with overly complex functions.
After-Sales Service: Choose brands and merchants with good after-sales service to ensure timely technical support and repair services in case of equipment failures. Understand the warranty policy, spare parts supply situation, etc., to guarantee the long-term stable use of the equipment.
VI. Key Points for the Use and Maintenance of Seedling Seeders
(A) Pre-Use Preparation
Seed Processing: Pre-treat the seeds by selecting, disinfecting, and germinating them to remove shriveled seeds and impurities, improve seed germination rates, and prevent the spread of pathogens.
Equipment Debugging: Adjust parameters such as seed dispensing quantity, sowing depth, and row spacing of the sower according to the characteristics of the seeds and planting requirements, and conduct a test run to ensure the equipment operates normally.
(B) Precautions During Use
Standardized Operation: Strictly follow the user manual for operation, maintaining a stable sowing speed and rhythm. When operating manual sowers, apply even force. For semi-automatic and fully automatic sowers, pay attention to controlling the traveling speed to avoid sudden stops and starts.
Real-Time Monitoring: During the sowing process, always observe the working status of the sower, such as whether the seed dispensing is smooth and whether the sowing depth is consistent. Stop the machine and adjust it immediately if any problems are found.
(C) Daily Maintenance and Care
Cleaning: After each use, promptly clean the sower to remove residual seeds, soil, and debris, preventing blockages and corrosion. Focus on cleaning components such as the seed dispensing mechanism, trencher, and soil cover.
Inspection and Lubrication: Regularly check whether the connections of various components are firm, whether the screws are loose, and whether the transmission components are worn. Lubricate key parts, such as the seed dispensing wheel shaft and transmission chain, to extend the service life of the equipment.
Long-Term Storage: During the non-use season, after a thorough cleaning and maintenance of the sower, store it in a dry and ventilated environment. If necessary, apply anti-rust treatment to metal components.
VII. Conclusion
With their unique working principles and notable advantages, Seedling Seeders have become important tools for improving efficiency and quality in the modern planting field. When purchasing, users need to consider factors such as their own planting needs, product quality, and budget to avoid common purchase pitfalls and select suitable equipment. At the same time, mastering the correct methods of use and maintenance can fully leverage the performance of Seedling Seeders, extend their service life, and provide strong guarantees for efficient and high-quality planting production. It is hoped that through the introduction in this article, everyone can better understand and utilize Seedling Seeders, embarking on a successful planting journey.

The CNC Seed Braiding Machine is a high-precision, fully automated agricultural equipment s...

It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...

The XP750 seeder has stable performance, excellent product quality, simple and convenient o...
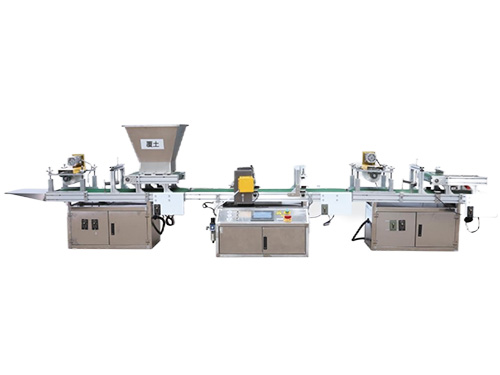
It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...