How to Use a Seedling Seeder: 5 Essential Efficient Operation Tips and Maintenance Methods for Beginners
2025-06-06 17:46:28
I. Introduction
(A) The Importance of Seedling seeder
In modern agricultural cultivation, Seedling seeder are crucial equipment for enhancing efficiency and ensuring precise sowing. Whether it's for the meticulous cultivation of a small home vegetable garden or the large-scale production of a commercial farm, they can save labor costs, guarantee uniform seed distribution, and lay a solid foundation for the healthy growth of crops.
(B) Purpose of the Article
This article aims to provide comprehensive guidance for beginners on using Seedling seeder. It will elaborate on 5 essential efficient operation tips and maintenance methods to help beginners quickly get started and extend the service life of the sowers.
II. Preparations Before Use
(A) Seed Treatment
Seed Selection: Through methods such as winnowing, water selection, and grain selection, pick out full, disease-free, and vigorous seeds, removing shriveled grains and impurities to ensure seed quality.
Seed Disinfection: Adopt common disinfection methods like hot water seed soaking and seed dressing with chemicals. Follow the operation steps strictly to prevent seeds from carrying pathogens that may affect seedling emergence.
Seed Germination Promotion: For seeds with difficult germination, use methods such as wrapping in wet cloths or placing in a constant-temperature box for germination promotion. Precisely control the humidity and temperature during the process.
(B) Sower Adjustment
Seed Discharge Rate Adjustment: Based on the size of different crop seeds and the requirements for planting density, adjust the seed discharge mechanism of the sower to control the number of seeds per hole.
Sowing Depth Adjustment: According to the characteristics of the seeds and soil conditions, adjust the depth of the opener's penetration into the soil and the pressure of the press wheel to ensure that the seeds are at an appropriate depth.
Row Spacing Adjustment: If the sower has a row spacing adjustment function, adjust it according to the planting plan to ensure uniform plant distribution and improve land utilization efficiency.
(C) Preparation of the Site and Auxiliary Tools
Site Cleaning: Thoroughly remove debris, stones, and weeds from the sowing site to ensure smooth movement of the sower and create a favorable environment for seed germination.
Auxiliary Tool Preparation: Prepare auxiliary tools such as containers for holding seeds, brushes for cleaning the sower, and wrenches for adjusting components, and clarify their uses.
III. 5 Essential Efficient Operation Tips
(A) Correct Sowing Posture and Rhythm
Manual Sowers: When using a handheld sower, maintain the correct grip and press it steadily with a uniform force and rhythm to avoid uneven sowing.
Semi-automatic and Automatic Sowers: When operating the equipment, either by driving or controlling it, maintain a stable traveling speed to prevent sudden stops and starts and ensure continuous sowing.
(B) Proper Addition of Seeds and Substrates (if applicable)
Seed Addition: Add seeds appropriately during the sowing process to keep an adequate amount of seeds in the seed box and avoid overfilling, which may cause blockages.
Substrate Addition (if applicable): When using a seedling substrate, ensure that it is loose and free of lumps. Add it evenly so that each sowing hole is filled with an appropriate amount of substrate.
(C) Coping with Different Terrains and Soil Conditions
Terrain Treatment: For special terrains such as slopes and low-lying areas, adjust the angle and traveling route of the sower to ensure uniform sowing.
Soil Condition Adaptation: Based on the soil's moisture level and texture, flexibly adjust the sowing depth and seed discharge rate to ensure successful seedling emergence.
(D) Real-time Monitoring and Adjustment
Observation of Sowing Conditions: During sowing, closely monitor the working state of the sower. Judge whether the seed discharge, depth, and row spacing are normal by observing the seed flow in the seed delivery tube and the traces on the ground after sowing.
Timely Parameter Adjustment: Once abnormalities such as missed sowing, double sowing, or inconsistent depth are found, immediately stop the machine, analyze the causes, and make adjustments.
(E) Multi-variety Mixed Sowing Techniques (if applicable)
Variety Mixing Principles: When conducting multi-variety mixed sowing, determine the mixing ratio based on the growth characteristics of the crops and market demand to achieve a combination of tall and short plants and crops with different maturity periods.
Sowing Sequence and Method: Clarify the placement sequence of different varieties of seeds in the sower. Adjust the settings of the seed discharge device to achieve proportional mixed sowing.
IV. Maintenance Methods
(A) Daily Maintenance
Cleaning the Sower: After each use, thoroughly clean components such as the seed box, seed discharge device, opener, and coverer to remove residual seeds, soil, and fertilizer.
Checking Component Connections: Inspect the connection parts of the sower, tighten loose screws and nuts, and repair cracks in welding areas.
Lubricating Key Parts: Regularly lubricate key parts such as the seed discharge wheel shaft, transmission chain, and opener rotating shaft with an appropriate lubricant.
(B) Regular Maintenance
Component Wear Inspection: Regularly check easily worn parts such as the seed discharge plate, the duckbill of the duckbill-type seed discharge device, and the rubber ring of the press wheel. Replace severely worn parts in a timely manner.
Calibration and Debugging: Before the start of each sowing season, recalibrate and debug parameters such as the seed discharge rate, sowing depth, and row spacing.
Electrical System Inspection (if applicable): For sowers equipped with an electrical system, regularly check the wires, plugs, and sensors, and replace damaged parts in a timely manner.
(C) Long-term Storage Maintenance
Thorough Cleaning and Drying: After the sowing season, comprehensively clean the sower and dry it to prevent rusting and mildew.
Disassembly and Storage: Disassemble removable parts and store them separately. Mark them for easy inspection and maintenance in the coming year.
Rust Prevention Treatment: Apply anti-rust agents or perform anti-rust spray painting on metal parts to avoid rusting and corrosion during long-term storage.
V. Common Problems and Solutions
(A) Sowing Faults
Poor Seed Discharge: Analyze causes such as seed hulls, impurity blockages, and seed discharge wheel jamming. Take targeted measures such as seed screening and cleaning the seed discharge port.
Inconsistent Sowing Depth: Investigate factors such as uneven soil, inconsistent resistance of the opener's penetration into the soil, and unbalanced suspension of the sower. Take measures such as leveling the land and adjusting the opener.
Missed Sowing or Double Sowing: Analyze causes from the aspects of seed adsorption performance, seed discharge device sealing, and transmission system stability. For example, adjust the vacuum degree and replace the sealing gasket.
(B) Equipment Damage
Component Wear: For worn parts such as the seed discharge plate and opener, introduce replacement methods and precautions, and guide the selection of appropriate replacement parts.
Mechanical Faults: Analyze the causes of mechanical faults such as broken transmission gears and damaged bearings. Explain the repair or replacement steps and seek professional help when necessary.
Electrical Faults (if applicable): Investigate the causes of electrical faults such as non-rotating motors and malfunctioning control systems, such as checking the power supply and wiring. Emphasize safety for non-professional personnel during operation.
VI. Conclusion
(A) Summary of Key Points
Recap the preparations before using the seedling sower, the 5 operation tips, maintenance methods, and solutions to common problems. Highlight the importance of correct use and maintenance for the sowing effect.
(B) Encouragement for Practice and Continuous Learning
Encourage beginners to apply the knowledge they have learned in actual operations, accumulate experience, and at the same time, pay attention to the development of seedling sowing technology. Continuously learn new skills and methods to achieve efficient and high-quality cultivation.
The above article covers the entire process of using a seedling sower. If you think certain parts need more detailed elaboration or have other suggestions for modification, please feel free to let me know.

The CNC Seed Braiding Machine is a high-precision, fully automated agricultural equipment s...

It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...

The XP750 seeder has stable performance, excellent product quality, simple and convenient o...
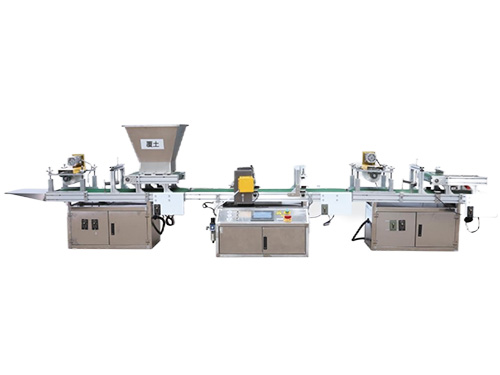
It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...