Demystifying Automatic Seedling Transplanters: Efficiency, Precision, and Support for Large-Scale Farming
2025-04-06 20:38:41
In the evolution of modern agriculture, the seedling transplantation phase serves as the crucial starting point for crop growth. The emergence of automatic seedling transplanters has brought revolutionary changes to large-scale farming, acting as a pivotal force in driving agricultural modernization with its efficiency and precision. Let’s delve into the secrets of this remarkable agricultural equipment.
I. Basic Understanding of Automatic Seedling Transplanters
1.Definition and Functions
An automatic seedling transplanter is a highly automated agricultural machinery designed to precisely distribute seeds into seedling containers or seedbeds during the seedling stage, following pre-programmed instructions. It integrates functions such as seed delivery, seeding rate control, seeding depth adjustment, and soil covering, significantly streamlining the seedling transplantation process.
2.Development History
Early seedling transplantation relied heavily on manual labor, which was inefficient and lacked precision. With technological advancements, simple mechanical seeding tools emerged, improving efficiency to some extent. However, the birth of automatic seedling transplanters, integrating modern mechatronics, sensor technology, and automation control, marked a leap from traditional manual operations to highly automated processes.
3.Working Principles
The operation of automatic seedling transplanters is based on a sophisticated automation control system. The power unit drives the seed metering mechanism, releasing seeds orderly from the storage bin through a seed delivery tube. Under sensor monitoring, seeds are accurately placed into designated positions. Simultaneously, the soil covering device applies the appropriate amount of soil over the seeds as per preset parameters. Different types of transplanters employ varied seed metering methods, such as pneumatic suction (using negative pressure to adsorb seeds for precise placement) or mechanical roller metering (ensuring quantitative seed output).
II. Notable Advantages of Automatic Seedling Transplanters
1.Efficient Operation, Time-Saving
Compared to traditional manual seeding, automatic transplanters significantly boost operation speed. They can complete large-area seedling transplantation tasks in a short time, shortening the seedling cycle and ensuring timely planting for optimal crop growth. This efficiency is particularly beneficial for large-scale farming, enhancing overall agricultural productivity.
2.Precise Seeding, Quality Assurance
Through precise control systems, automatic transplanters strictly adhere to preset seeding rates, depths, and row spacing. This ensures each seed is placed in an optimal growth environment, promoting uniform seedling emergence and growth. Precise seeding reduces seed waste and facilitates subsequent field management tasks like irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, thereby improving crop yield and quality.
3.Reduced Labor Intensity, Optimized Labor Costs
Manual seedling transplantation requires prolonged bending and strenuous labor. Automatic transplanters allow operators to simply set parameters and monitor the process from a control console, eliminating heavy physical work. This not only alleviates labor burdens but also optimizes labor costs, making agricultural production more efficient and manageable.
III. Key Considerations for Choosing Automatic Seedling Transplanters
1.Selection Based on Farming Scale
Small-Scale Farmers: For small planting areas, compact, lightweight, and user-friendly transplanters are suitable. These machines are affordable and flexible for small fields or greenhouses, meeting small-scale seedling needs.
Medium-Sized Farms: Medium-sized operations require transplanters with high efficiency and multifunctionality. Models compatible with medium-power equipment can handle larger areas and may include synchronized fertilization and soil compaction functions.
Large Agricultural Enterprises: For expansive farms, large-scale, highly automated transplanters with wide working widths and rapid seeding speeds are ideal. These machines can complete large-scale tasks quickly and feature high intelligence, enabling remote monitoring and precise parameter adjustments.
2.Selection Based on Crop Type
Vegetable Seedlings: Vegetable seeds vary in size and shape, with some being costly. For vegetables, opt for transplanters with precise metering mechanisms to ensure accurate placement and minimize waste.
Flower Seedlings: Flower seeds are often tiny, requiring strict depth and uniformity. Choose transplanters with fine-tuning capabilities for shallow, precise seeding to enhance success rates.
Grain Crop Seedlings: Grain seeds are relatively large, and their seedling environments are more robust. Select transplanters with strong metering force and adjustable seeding depth ranges to accommodate diverse grain seed requirements.
3.Budget-Based Decisions
Low-Budget Options: For limited budgets, basic transplanters with simple functions suffice. Though feature-limited, they meet essential seeding needs, suitable for startups or smallholders.
Mid-Range Choices: With moderate budgets, opt for transplanters with better performance and multifunctionality (e.g., combined seeding and soil covering, basic diagnostics) to improve efficiency and reliability.
High-End Configurations: For ample budgets, invest in advanced, intelligent transplanters. These machines offer superior precision, efficiency, and IoT integration for remote monitoring and data analysis, providing long-term returns for large-scale modern farms.
IV. Usage and Maintenance Tips for Automatic Seedling Transplanters
1.Pre-Use Preparations
Comprehensive Inspection: Before use, check all components for damage, looseness, or deformation, ensuring the machine is in working order.
Calibration: Fine-tune the metering system based on seed type and seeding rate requirements. Conduct trial runs to adjust parameters for accuracy.
Cleaning and Lubrication: Remove debris, dust, and grease from the machine. Lubricate transmission parts (chains, gears, bearings) to ensure smooth operation.
2.Operational Best Practices
Speed Control: Adjust seeding speed according to soil type and moisture. Increase speed in loose soil; reduce speed in heavy or dry soil to avoid uneven depth or missed seeds.
Row Spacing Adjustment: Strictly follow crop agronomic requirements to set row spacing. Monitor stability during operation and adjust promptly if deviations occur.
Depth Flexibility: Adjust seeding depth based on seed size, crop type, and soil conditions. Large seeds can be planted deeper; small seeds require shallow placement. Adjust depth according to soil moisture.
3.Routine Maintenance
Timely Cleaning: After each use, clean soil, weeds, and seed residues to prevent blockages, especially in metering devices and delivery tubes.
Regular Lubrication: Lubricate all points periodically, focusing on wear-prone parts (chains, universal joints, bearings) to extend lifespan.
Component Inspection and Replacement: Check wear on metering disks, opener shares, and covering discs. Replace damaged parts and tighten loose bolts to ensure structural integrity.
V.Conclusion
With their efficiency and precision, automatic seedling transplanters provide robust support for large-scale farming. For farmers, understanding their advantages, selecting appropriate models, and mastering proper usage and maintenance will maximize their effectiveness, boosting agricultural productivity and driving modernization. In the future, these transplanters will play an increasingly vital role in agricultural development, propelling the industry to new heights.

It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...

The XP750 seeder has stable performance, excellent product quality, simple and convenient o...
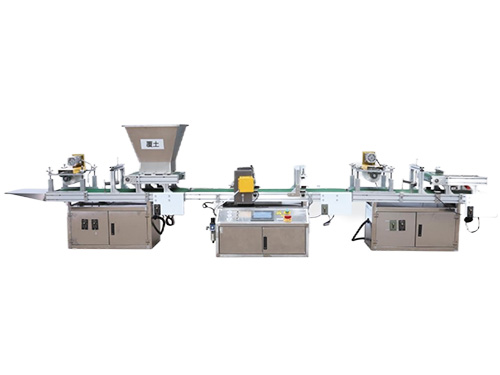
It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...

Needle list Seed nozzle model Different models Sowing types are different...