High-Quality Seedling Trays and Propagation Trays: Safeguarding the Growth of Seedlings
2025-04-02 05:58:30
As the foundation of the national economy, agriculture holds undeniable importance. Among the entire agricultural production process, the sowing and seedling stages are undeniably critical, directly determining the growth conditions of crops and the final harvest. High-quality seedling trays and propagation trays serve as robust guardians for the growth of seedlings, playing a crucial role in enhancing seedling efficiency and ensuring seedling quality.
The Importance of Seedling Trays and Propagation Trays
Enhancing Seedling Efficiency
Traditional open seedling methods involve scattered seeds, making management difficult and time-consuming. The emergence of seedling trays and propagation trays has streamlined the seedling process, making it orderly and centralized. With their grid design, these trays allow for the cultivation of a large number of seedlings at once, enabling batch seedling production. Staff can efficiently perform sowing, watering, and fertilization operations, significantly shortening the seedling cycle and allowing land resources to be utilized more quickly in the next stage, thereby enhancing overall seedling efficiency.
Ensuring Seedling Quality
High-quality trays provide a stable and suitable growth environment for seedlings. The grids in the trays give each seedling independent growth space, preventing root entanglement and nutrient competition among seedlings. At the same time, the excellent drainage and air permeability of the trays help maintain optimal soil moisture and oxygen levels, promoting healthy root growth and fostering stronger, more uniform seedlings, laying a solid foundation for the later growth and high yields of crops
How to Choose Suitable Seedling Trays and Propagation Trays
Consider the Type of Crop
Different crops have varying seed sizes, germination characteristics, and seedling growth habits. For example, for large bean seeds, it is suitable to use trays with larger, deeper grids to provide sufficient space for germination and rooting. For small vegetable seeds like celery and carrots, trays with small, shallow grids are needed to prevent seed clustering and ensure uniform sowing. For flowering plants that require high soil air permeability, paper or highly breathable plastic trays can be chosen.
Seedling Scale
For small-scale farmers or home gardeners with a small number of seedlings, small, easy-to-operate trays such as individual or combined plastic suction-molded trays are suitable, being cost-effective and easy to manage. For large-scale commercial seedling bases requiring large quantities of seedlings, priority should be given to durable injection-molded plastic trays or large foam trays that can handle batch operations, improving work efficiency and reducing unit seedling costs.
Budget Considerations
The price of trays varies with material, size, and manufacturing process. Plastic trays are relatively affordable, with suction-molded trays being the cheapest, suitable for budget-conscious users. Although injection-molded trays are slightly more expensive, they are durable and have lower long-term costs. Paper trays, due to their eco-friendly features and special functions, are usually more expensive and suitable for environmentally conscious seedling projects with sufficient budgets. When choosing, it is important to comprehensively consider the price, lifespan, and seedling effects of the trays, weighing cost-effectiveness and avoiding making decisions solely based on price.
Physical Characteristics of Trays
Drainage and Air Permeability
Good drainage and air permeability are key to ensuring healthy seedling growth. The size and number of drainage holes at the bottom of the tray should be appropriate, allowing timely drainage of excess water to prevent root rot while maintaining soil moisture. For air permeability, plastic trays can be equipped with air holes on the tray walls or use special breathable materials. Paper trays have inherent breathability. For foam trays, attention should be paid to the impact of their internal structure on air circulation. When choosing, select trays with suitable drainage and air permeability based on the humidity and air requirements of the seedlings.
Size and Grid Design
The size of the tray should be determined based on the space of the seedling site and the seedling method. For example, in greenhouses, consider whether the trays can be matched with existing seedling racks and irrigation equipment. The size and shape of the grids should match the size and growth characteristics of the seeds and seedlings. If the grids are too small, seedling growth space will be limited; if they are too large, space will be wasted and uniform management will be hindered. A reasonable grid design also facilitates marking and classification management of seedlings.
Proper Use and Operation of Seedling Trays and Propagation Trays
Preparations Before Sowing
Tray Cleaning and Disinfection
Before using the trays, thoroughly clean them to remove surface dust, impurities, and residual soil. Rinse with clean water, then soak or spray with disinfectant to kill any potential pathogens and insect eggs, providing a clean, sterile growth environment for the seeds. After disinfection, dry the trays for later use.
Substrate Preparation and Filling
Select appropriate seedling substrates such as nutrient soil, vermiculite, and perlite, and mix them in a certain proportion to ensure good fertility, air permeability, and water retention. Fill the prepared substrate evenly into the tray grids, with the filling amount being moderate, generally slightly below the grid edge, to facilitate subsequent sowing and covering operations. After filling, lightly press the substrate to make it compact but not too tight, ensuring good contact between the seeds and the substrate.
Key Points During Sowing
Sowing Methods
Choose suitable sowing methods based on seed size and characteristics. For large seeds, use the dibbling method, placing seeds one by one into the center of the tray grids with tweezers or fingers. For small seeds, mix the seeds with an appropriate amount of fine sand and broadcast them evenly on the trays, then cover with a thin layer of soil. The sowing depth should be determined based on seed size and germination characteristics, with large seeds sown deeper and small seeds sown shallower. After sowing, lightly cover with a thin layer of soil, just enough to cover the seeds, then water appropriately to keep the soil moist.
Labeling
After sowing, promptly label the trays with information such as seed variety and sowing date for subsequent management and identification. Labels can be plastic or paper, written with waterproof pens to ensure clear and lasting information.
Post-Sowing Management
Water Management
Maintaining optimal soil moisture in the trays is crucial for seedling growth. Before seedling emergence, keep the soil moist but avoid waterlogging, watering appropriately according to weather conditions and soil moisture. Generally, use a spray watering method to evenly moisten the soil without washing away seeds and substrate. After seedling emergence, gradually reduce watering frequency and increase watering amount, following the principle of "dry and wet alternation" to promote downward root growth.
Temperature and Light Adjustment
Adjust the temperature and lighting of the seedling environment based on the growth habits of the seedlings. Most seeds require a suitable temperature for germination, generally between 20 - 30 degrees Celsius. Temperature can be controlled by covering with a thermal film or adjusting ventilation. In terms of lighting, some seeds require sufficient light to germinate, while others require shading. For seeds requiring light, place the trays in a well-lit area but avoid direct sunlight. For seeds requiring shading, cover the trays with a layer of black plastic film or shading cloth.
Maintenance and Care of Seedling Trays and Propagation Trays
Cleaning After Use
After each use, promptly clean residual soil, seedling roots, and debris from the trays. Rinse with clean water. For stubborn stains, gently scrub with a soft brush. After cleaning, place the trays in a well-ventilated area to dry, avoiding prolonged humidity to prevent mold and bacterial growth.
Regular Inspection and Repair
Regularly inspect the trays for damage, deformation, etc. For plastic trays, if cracks or damage are found, use plastic welding tools for repair. For paper trays, if they are severely damaged and cannot be repaired, replace them promptly. Check if the drainage holes of the trays are blocked. If blocked, clean them promptly to ensure smooth drainage. At the same time, check if the grids of the trays are loose. If loose, use glue or other fixing materials for reinforcement.
Long-Term Storage Precautions
If the trays need to be stored for a long time, clean and dry them thoroughly before neatly stacking or classifying them for storage. For plastic trays, place some soft cushioning materials such as foam boards or cardboard between the trays to prevent deformation from mutual pressure during stacking. Store paper trays in a dry, ventilated environment to avoid moisture and mold. Keep them away from fire sources and chemicals to prevent damage.
Conclusion
High-quality seedling trays and propagation trays play an indispensable role in the agricultural seedling field. They not only improve seedling efficiency and ensure seedling quality but also lay a solid foundation for high crop yields. By correctly selecting, using, and maintaining trays, and keeping up with industry development trends, agricultural practitioners can achieve efficient production in seedling work, injecting new vitality into the sustainable development of the agricultural industry. In the future, with continuous technological progress and innovation, seedling trays and propagation trays will continue to be optimized and upgraded, providing stronger support for the agricultural modernization process.

It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...

The XP750 seeder has stable performance, excellent product quality, simple and convenient o...
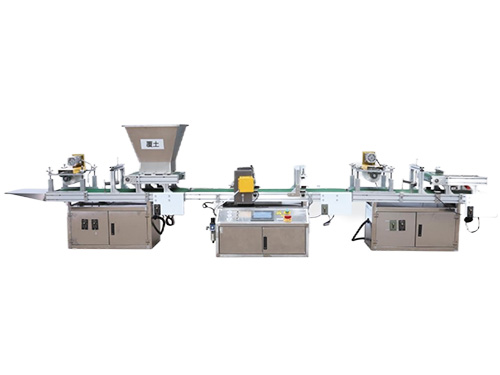
It adopts electrical integration and can be started by pressing the fully automatic button ...

Needle list Seed nozzle model Different models Sowing types are different...